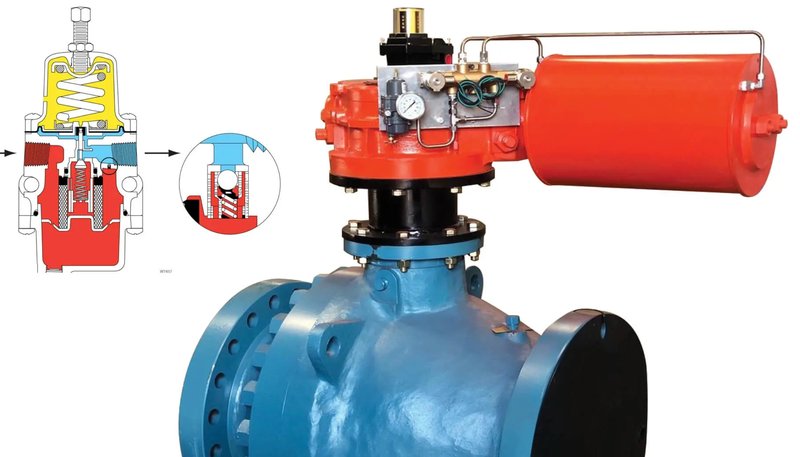
Maintenance of pneumatic valves is essential to ensure their long-term stable operation. The following are some maintenance recommendations:
Regular inspection: Regularly inspect the valve's sealing surfaces, stem and actuator in working condition to ensure that there is no wear and corrosion.
Cleaning: Keep the valve and its surroundings clean to prevent dust and impurities from affecting the normal operation of the valve.
Lubrication: Regularly lubricate the valve stem and other moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
Air source management: Ensure the cleanliness of the air source to avoid moisture and impurities from entering the pneumatic system.
Pneumatic valve suitable for what pipeline
Pneumatic valves have a wide range of applications in piping systems and are suitable for many types of pipelines. The following is a detailed description of the types of piping for which pneumatic valves are suitable and their application scenarios:
1. Water pipelines
Pneumatic valves are common in water treatment and water supply systems and are mainly used to control water flow and pressure. These valves are able to respond quickly Pneumatic valves can effectively prevent the phenomenon of negative pressure in the pipeline, to avoid the risk of pipe rupture or contamination.
Application examples: water treatment plants, water supply networks, fire-fighting systems, etc.
2. Sewage pipeline
In the sewage treatment process, pneumatic valves are used to control the flow of sewage and various chemicals in the treatment process. They can withstand corrosive media and operate stably under high pressure conditions.
Application examples: sewage treatment plants, sewage transport pipelines, etc.
3. Chemical pipelines
Pneumatic valves are used in the chemical industry to control the flow of various chemical substances. These valves are usually made of corrosion-resistant materials and are able to adapt to harsh working environments.
Application examples: chemical production lines, chemical reactors, storage tanks, etc.
4. Oil and gas pipelines
Pneumatic valves are used in the oil and gas industry to control the transport and handling of oil and gas. They are often used for emergency shutdown and safety control to ensure the safety and reliability of the system.
Application examples: oil and gas pipelines, refineries, storage tanks, etc.
What are the applications of pneumatic actuators
Chemical industry: Pneumatic actuators are used in chemical production to control the flow and pressure of chemicals to ensure the safety and stability of the production process, especially in flammable and explosive environments, where pneumatic actuators have an advantage due to their safety.
Water treatment: In water treatment plants, pneumatic actuators are used to control valves and regulate water flow and quality to ensure the efficiency and safety of the water treatment process.
Food Processing: Pneumatic actuators are widely used in food and beverage production lines for their low risk of contamination, enabling effective control of fluids and gases in the production process.
Manufacturing: Pneumatic actuators are used in automated production lines to drive robotic arms and other automated equipment, favoured for their fast response and simple maintenance.
Power Plants: Pneumatic actuators are used in power plants to control the flow of steam and water, ensuring the stability and efficiency of the power generation process, and are suitable for high temperature and high pressure environments.
Electronics industry: In the manufacturing and assembly of electronic components, pneumatic actuators provide precise positioning and fast movements to meet the demands of rapid production.
Pneumatic actuators play an important role in a number of industries due to their high efficiency, safety and economic characteristics, promoting the development of automation technology.