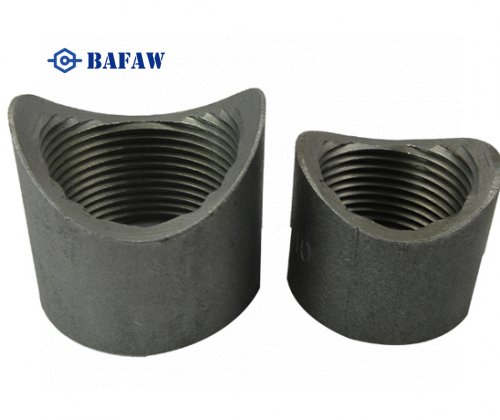
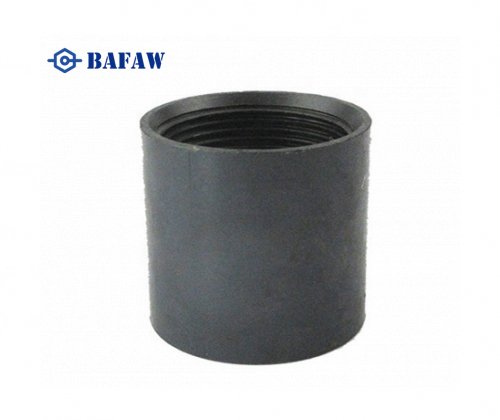
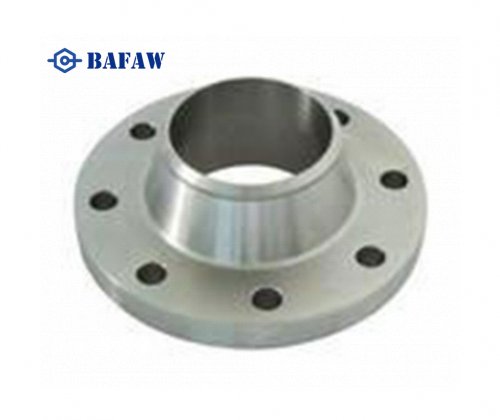
Welding lap joint flanges is a crucial process in the assembly of piping systems. It requires precision and adherence to specific techniques to ensure the integrity and reliability of the joints. Lap joint flanges consist of two main components: the stub end and the backing flange. The stub end is welded to the pipe, while the backing flange is free to rotate around the stub end, allowing for easy alignment during assembly. Welding these components together requires careful consideration of the materials, welding techniques, and environmental factors to ensure a secure and leak-free joint.
Step-by-Step Welding Process
1. Preparation
Before initiating the welding process, it is essential to prepare the surfaces to be welded. This involves cleaning the mating surfaces of the stub end and backing flange to remove any contaminants, scale, or oxides that could compromise the quality of the weld. Proper surface preparation is critical for achieving a strong bond between the components.

2. Alignment
Once the surfaces are prepared, align the stub end and backing flange to ensure proper fit and alignment of the bolt holes. The ability to rotate the backing flange allows for easy adjustment to achieve precise alignment before welding.
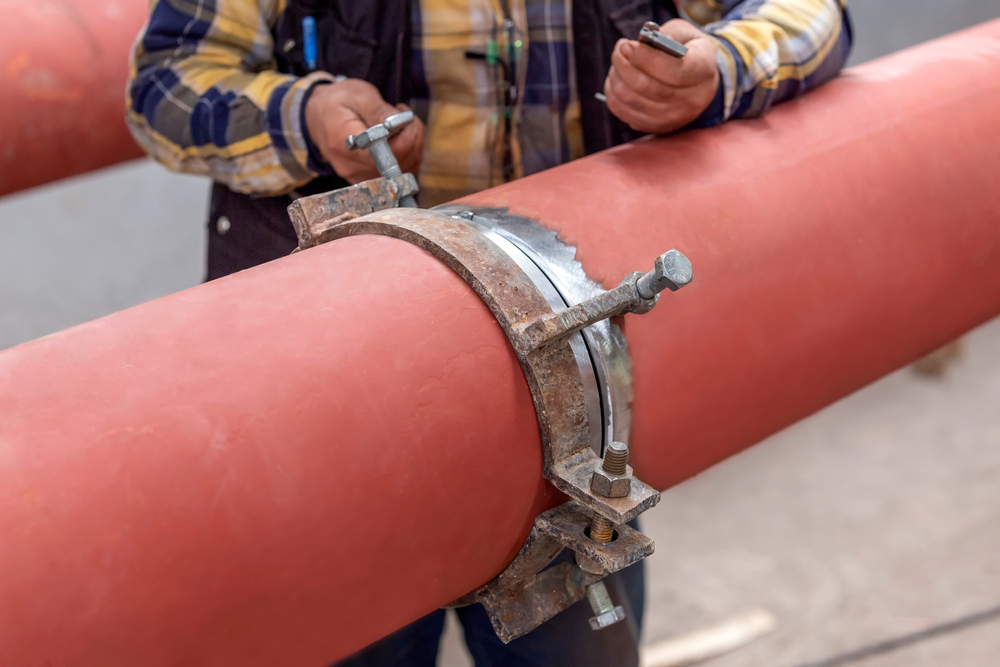

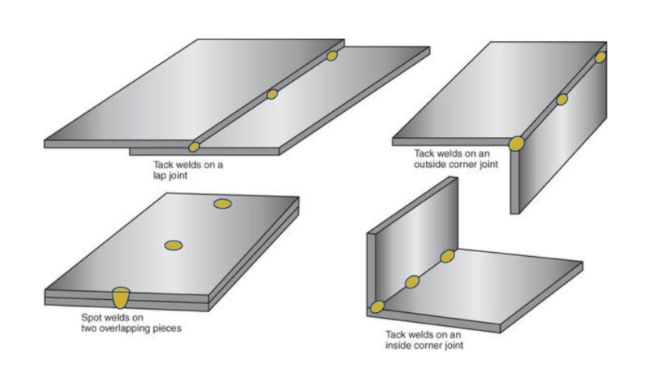
3. Tack Welding
Tack welding is used to temporarily secure the stub end and backing flange in place before the final welding. Tack welds should be strategically placed to maintain alignment and prevent distortion during the welding process.
4. Welding Technique
The welding technique employed for lap joint flanges is typically fillet welding. This involves creating a weld fillet along the intersection of the stub end and backing flange. Careful attention should be given to the welding parameters, such as current, voltage, and travel speed, to ensure proper penetration and fusion of the weld joint.

5. Post-Weld Inspection
After completing the weld, it is crucial to conduct a thorough inspection to assess the quality of the weld joint. Visual inspection, dye penetrant testing, or radiographic testing may be performed to detect any defects or discontinuities in the weld.

To achieve high-quality welds on lap joint flanges, consider the following best practices:
1. Use compatible materials for the stub end, backing flange, and filler metal to ensure metallurgical compatibility and prevent galvanic corrosion.
2. Employ proper welding techniques, such as back purging, to minimize the formation of weld defects and ensure sound welds.
3. Adhere to industry standards and codes, such as ASME B31.3 and AWS D1.1, to meet regulatory requirements and ensure the structural integrity of the weld joint.
Welding lap joint flanges demands precision, attention to detail, and adherence to best practices to achieve strong and reliable joints. By following the step-by-step welding process and implementing best practices, welders can ensure the integrity and performance of lap joint flange assemblies in various piping applications.
For more information about welding techniques and best practices for flange assemblies, visit bestflowvalve.
Remember, proper welding procedures are essential for the safety and functionality of piping systems. Always consult qualified professionals and adhere to industry standards when performing welding operations.
















































